Diabetics with foot wounds should be wary of using hydrocolloid wound dressings.
Wound care is a complex process made more efficient by a variety of means, from having proper nutrition to keeping stress levels low. The type of products you, with the guidance of your clinician, choose to dress the wound has the greatest impact. There are a plethora of traditional and advanced dressings, and one commonly used is the hydrocolloid dressing. Learn more about this advanced wound care category so you and you clinician can make an informed decision about whether a hydrocolloid dressing is right for you.
What are hydrocolloid dressings?
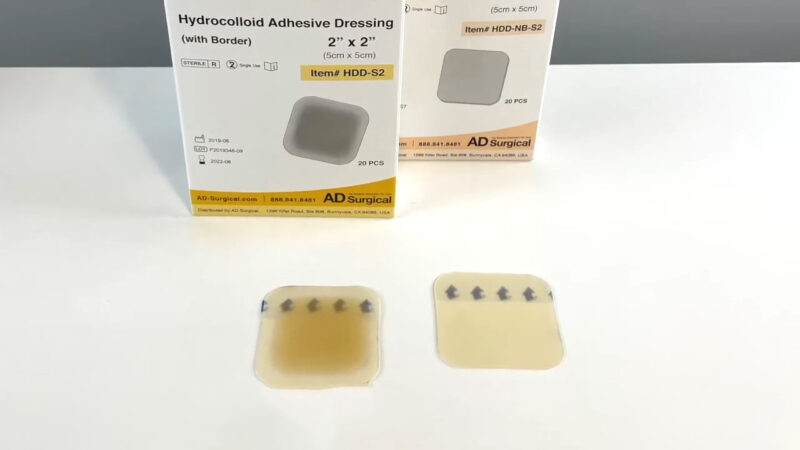
Hydrocolloid dressings have a unique design. They contain gel-forming agents (a gelatin or sodium carboxymethylcellulose) held within an adhesive compound, which is laminated in place on a foam or film, generally made of polyurethane. The end product is an advanced wound dressing that resembles an absorbent, flexible wafer typically both waterproof and self-adhering.
The aim of this type of dressing is to provide a moist healing environment and insulation while using the body’s own moisture and enzymes to keep the wound bed hydrated for proper wound healing. The dressing does this by absorbing wound exudate and forming a gel, and the properties of the gel depend on the agents contained within the compound; one may create a cohesive coagulate, while another might produce a less viscous, waterier gel. These products are generally available with or without adhesive borders and in a wide variety of thicknesses.
When do I use hydrocolloid dressings?
These dressings can be used on many different types of wounds, and they have the best effects on those that are uninfected, of partial or full thickness and have low to moderate drainage. Clinicians often suggest hydrocolloid dressings for granular and necrotic wounds, as the products protect intact and newly healed skin. These wound dressings may not be suitable for wounds with high exudate.
What are the advantages and disadvantages?
Hydrocolloid dressings come with a multitude of benefits, including these main advantages:
- Impermeable to protect against bacteria and other outside invaders
- Doesn’t adhere to the wound, only the surrounding skin, thereby keeping healed skin intact
- Easy to apply to wound site
- Can be used in conjunction with venous compression products
- Minimal disruption to healing as it needs to be changed only once every several days
These wound dressings also come with a variety of disadvantages, including:
- Not intended for wounds with infection, sinus tracts or heavy exudate
- Can become dislodged in the case of heavy exudate
- Wound assessments made more difficult by opaque hydrocolloids
- Can roll up or curl at the edges
- Dressing residue can stick to the wound bed and cause an unpleasant odor after dressing removal
- May lead to hypergranulation
- Skin around the wound may begin to macerate
People considering using these wound dressings should keep in mind that they must be used with great caution when applied to the feet of diabetics. As Wound Care Advisor points out, they should only be used after an exhaustive patient assessment has been conducted, there is no sign of infection or ischemia, the wound is superficial and there is low to moderate exudate. Even then, the dressings should be changed frequently.
How do I apply hydrocolloid dressings?
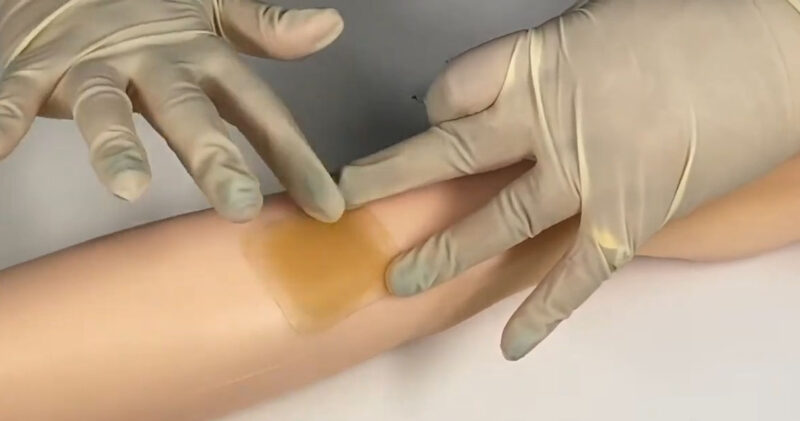
While your clinician may suggest additional or alternative steps for your particular wound, this is the general process for applying a hydrocolloid dressing:
- Clean the wound with saline solution.
- Dry the skin surrounding the wound with sterile gauze.
- After removing the paper carrier, center the dressing over the wound site and apply to surrounding skin with a rolling motion to smooth out the edges.
- Unless the dressing has its own border, frame it with tape.
Advanced Tissue carries a wide variety of hydrocolloid dressings including:
Advanced Tissue offers an extensive range of hydrocolloid dressings, each designed to cater to specific wound care needs. Our selection includes renowned brands and products, ensuring you have access to high-quality options for optimal wound healing and management. Some of the hydrocolloid dressings we provide include:
- Tegaderm: Tegaderm hydrocolloid dressings are known for their excellent moisture management properties. They create an optimal healing environment for wounds while offering a breathable and transparent barrier.
- Comfeel Plus: Comfeel Plus dressings are designed to provide superior absorption and protection for moderate to heavily exuding wounds. They offer a comfortable and conformable fit.
- Duoderm: Duoderm hydrocolloid dressings are trusted for their versatility in managing various wound types. They promote a moist wound environment to support the natural healing process.
- Medihoney: Medihoney dressings harness the natural antibacterial properties of honey to aid in wound healing. They are ideal for chronic wounds and those with infection concerns.
- Restore: Restore hydrocolloid dressings are crafted to minimize skin damage during removal while effectively managing exudate. They are gentle on the skin, making them suitable for sensitive patients.
- Replicare: Replicare dressings are known for their high absorption capacity and conformability. They are especially useful for wounds with irregular contours and high exudate levels.
- Nuderm: Nuderm dressings offer a discreet and low-profile solution for wound care. They are designed to adhere securely to the skin while providing effective moisture management.
FAQ
Are hydrocolloid dressings suitable for all types of wounds?
No, they work best for uninfected wounds with low to moderate drainage, usually partial or full thickness.
Can hydrocolloid dressings be used on diabetic foot wounds?
They should be used cautiously on diabetic foot wounds after thorough assessment and in specific conditions.
How often should I change a hydrocolloid dressing?
Typically, these dressings need to be changed every several days, but your clinician may recommend a different schedule.
Do hydrocolloid dressings cause discomfort when removed?
They can sometimes stick to the wound bed, which may cause discomfort and an unpleasant odor during removal.
Are hydrocolloid dressings transparent?
No, they are opaque, which can make wound assessments more challenging.
Can hydrocolloid dressings be used with infections?
They are not intended for wounds with infections or sinus tracts.
Do hydrocolloid dressings work well with high-exudate wounds?
No, they are not suitable for wounds with heavy exudate.
Final Words
Hydrocolloid dressings are a valuable option for wound care, offering benefits like protection and minimal disruption to healing. However, they may not be suitable for all wound types, and caution should be exercised, especially with diabetic foot wounds.