From abrasions, lacerations, punctures, and more, there are many types of wounds that can damage the skin and keep it from remaining the protective barrier that keeps your body safe from infection, even including radiation exposure and other harmful chemicals. When healing is the only thing on your mind, the road to recovery can seem like a long one. Are antibiotics your ticket to wellness?
According to Drugs.com, antibiotics are defined as medicines that stop or prevent bacteria growth and keep it from leading to an infection. Antibiotics are available in various forms, from oral tabs and sprays to creams, ointments, and powders.
In this article, we’ll discuss when you need to consider an antibiotic, plus the easiest way to ensure proper recovery: hygiene.
How do I know if I have an infection?
In most cases, a wound can heal properly without help from an antibiotic. When it becomes infected, it should raise concern. The following signs may point to an infection:
- The skin around the wound is warm, according to Medical News Today.
- There’s an unpleasant odor and discharge coming from the area.
- You’re experiencing fever, chills, aches, pains, nausea, and vomiting.
What are Some Common Antibiotics for Wound Infections?
The type of antibiotic you are prescribed for a wound infection will depend on a number of factors, such as:
- The cause of your wound’s infection
- Any allergies you have
- Your overall general health
- The antibiotic’s interaction with other medications you may be taking
Here are some common antibiotics:
Topical Antibiotics

- Bacitracin
- Neomycin
- Polymyxin B
- Mupirocin
- Nitrofurazone
- Fusidic acid
Oral Antibiotics

- Amoxicillin-clavulanate
- Cephalexin
- Clindamycin
- Dicloxacillin
- Doxycycline
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
IV Antibiotics
- Cephalosporins
- Penicillin
- Fluoroquinolones
- Nitroimidazoles
- Glycopeptides
- Oxazolidinone
- Carbapenems
The dosage of antibiotics varies depending on the patient, the severity of their infection, and the type of microorganism that has caused the infection.
It is important that patients follow doctors’ guidelines and complete the entire course of antibiotics, whether or not they feel better by day 3 or 4 of their treatment.
The Truth About Antibiotics
Most skin infections can be treated with standard hygiene, such as washing with soap and water. The severity of the wound plays a major role in whether an antibiotic may be beneficial. Wounds UK, a major international healthcare business with specialization in wound management, believes there is limited research to support the claim that antibiotics have the power to heal; rather, they can prevent wound infection that could put the healing process on hold.
At the end of the day, it’s always best to trust the judgment of your medical professional and take his or her advice before making your decision about antibiotics.
Take Care of Your Wound at Home
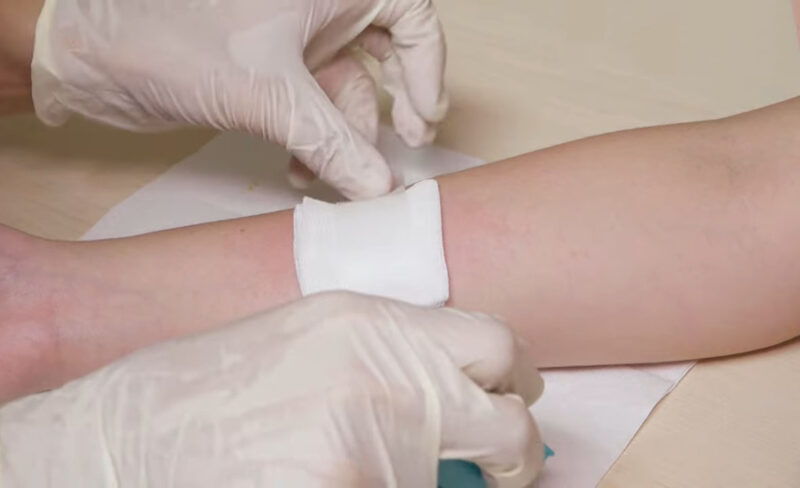
While taking an antibiotic during the early stages of wound care can be beneficial to recovery, the simple act of keeping the injury clean can make a major difference and reduce your risk of infection. SmartPAC by Advanced Tissue enables you to take care of your wound independently from the comfort of your own home. The packaging is designed to help you feel more confident about taking control of your healing process; each package comes with individually dosed supplies and on-demand videos that guide you through your daily dressing changes.
Antiseptic Usage In Wound Management
Unlike antibiotics, which are designed to combat specific pathogens, antiseptics have a wider range of effectiveness as they can target various microorganisms. Applied directly to wounds, antiseptic solutions play a crucial role in reducing the number of microbes present, aiding in the healing process. Antiseptics are increasingly favored in wound management due to their lower resistance rates. Here are some commonly used antiseptic agents:
- Iodine: Cadexomer iodine not only creates a favorable moist environment for wound healing but is also an efficient agent against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown to accelerate wound healing, though its use is recommended for short durations.
- Polyhexanide: Gaining popularity in wound care, polyhexanide stands out for its minimal toxicity. It works effectively as an antiseptic without hindering the natural process of wound healing and is more effective than iodine-based antiseptics. It’s particularly successful in eliminating Methicillin-Resistant Staph Aureus (MRSA).
- Silver-based agents: Known for their antibacterial properties, silver agents are used to lessen bacterial load in wounds. Despite their ability to inhibit bacterial growth, silver agents are not significantly more effective in promoting wound healing compared to other methods. Additionally, their high toxicity to fibroblasts and keratinocytes warrants cautious use.
FAQ
1. Can natural remedies be effective in wound healing?
While some natural remedies may offer mild antiseptic properties, they should not replace medical treatment, especially for serious wounds or infections.
2. How long should a wound be monitored before seeking medical attention?
It’s advisable to seek medical attention if a wound shows no signs of improvement within a few days or if symptoms of infection appear.
3. Are there dietary considerations that can aid in wound healing?
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly Vitamin C and Zinc, can support the body’s natural healing processes.
4. Can overuse of antibiotics lead to resistance?
Yes, overusing antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance, making it crucial to use them only as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
5. Is it safe to use alcohol as an antiseptic on wounds?
Alcohol can be too harsh on wounds, potentially damaging tissue and delaying healing. Gentler antiseptics are usually recommended.
6. How do I care for a wound treated with antibiotics?
Keep the area clean and dry, follow the prescribed antibiotic regimen, and watch for signs of allergic reactions or worsening symptoms.
7. Can chronic health conditions affect wound healing?
Conditions like diabetes or circulatory problems can slow down wound healing, making careful monitoring and specialized care important.
Bottom Line
Effectively managing wounds, whether through antibiotics, antiseptics, or standard hygiene practices, plays a vital role in promoting healing and preventing infections. Understanding the type of wound, its severity, and the appropriate treatment options is crucial.
Remember, the guidance of healthcare professionals is paramount in making informed decisions about wound care. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve a safe and speedy recovery, balancing medical intervention with proper home care and lifestyle adjustments.